Защита Spring Boot RESTful Service используя Basic Authentication
1. Цель примера
Статья основана на:
Spring Boot 2.x (Or >= 1.5.9)
Eclipse 4.7 Oxygen
Смотрите также:
В данной статье я покажу вам как создать приложение RESTful Web Service и защитить его с помощью Basic Authentication. Это значит ваше приложение будет предоставлять ресурсы данных (Resource), но пользователь, который захочет использовать данный ресурс данных должен аутентифицироваться (authenticate) с методом базовой аутентификации (Basic Authentication).
Basic Authentication (Базовая аутентификация)
Чтобы получить доступ к ресурсам (Resource) защищенные Basic Authentication, пользователь должен отправить request и в том request должна содержаться информация username/password прикрепленная на Header.
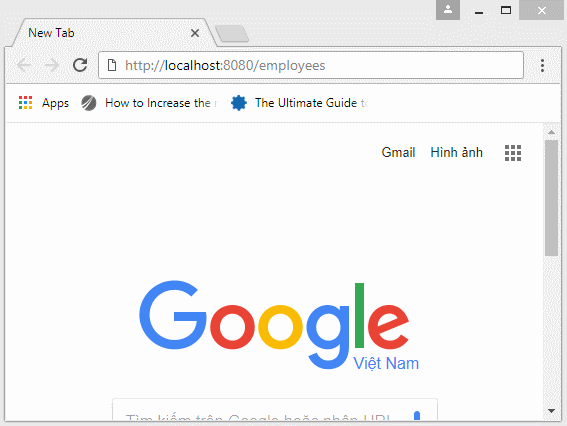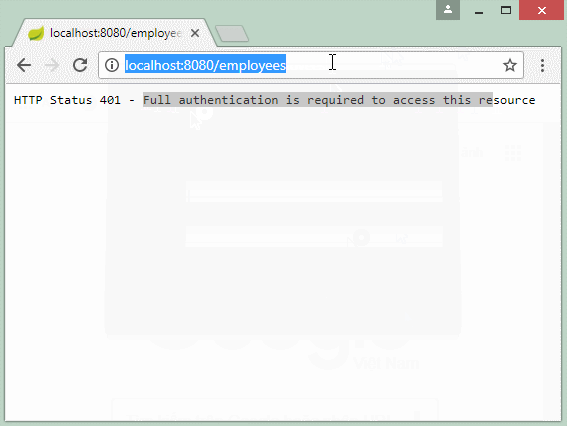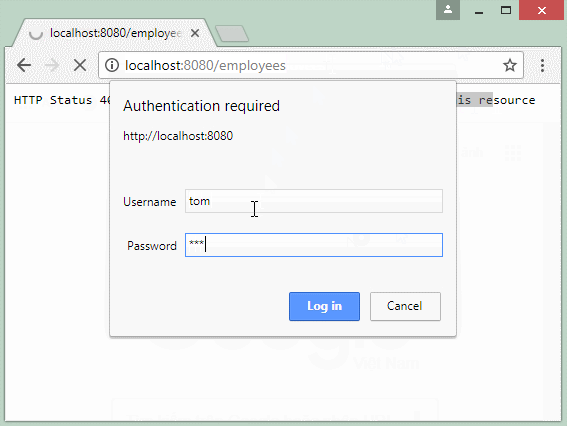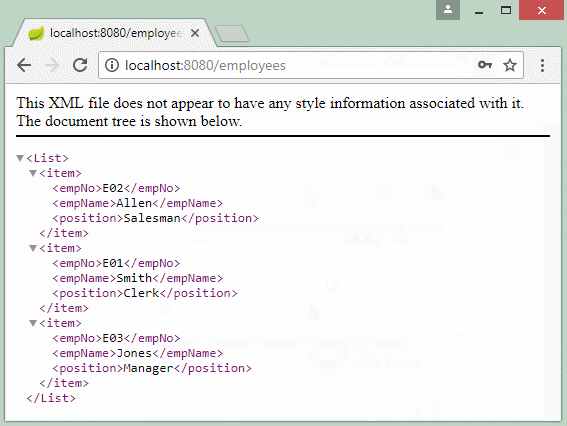
Вы можете использовать браузер для доступа в ресурс данных, защищенный Basic Authentication, в данном случае отображается диалог (dialog), который позволит вам ввести username/password, данная информация прикрепляется в request чтобы отправить на REST Server.
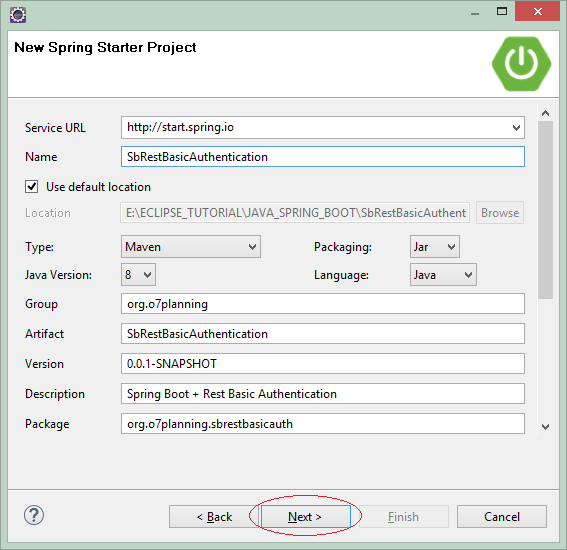
2. Создать Spring Boot project
На Eclipse создать проект Spring Boot.
Ввести:
- Name: SbRestBasicAuthentication
- Group: org.o7planning
- Package: org.o7planning.sbrestbasicauth
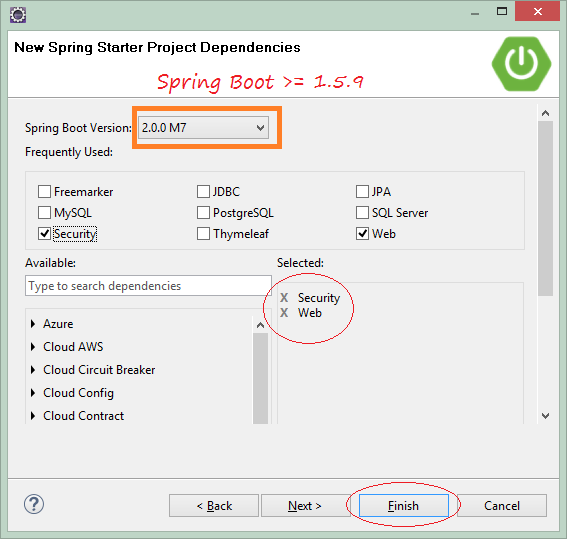
Следующий шаг, вам нужно выбрать технологии использования.
SbRestBasicAuthenticationApplication.java
package org.o7planning.sbrestbasicauth;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class SbRestBasicAuthenticationApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SbRestBasicAuthenticationApplication.class, args);
}
}3. Конфигурация pom.xml
В данном примере нам нужна библиотека для конвертирования (convert) XML в объект Java и обратно. И другая библиотека для конвертирования JSON в Java и обратно.
JSON <==> Java
spring-boot-starter-web имеет готовую библиотеку jackson-databind, данная библиотека помогает конвертировать JSON в объект Java и обратно.
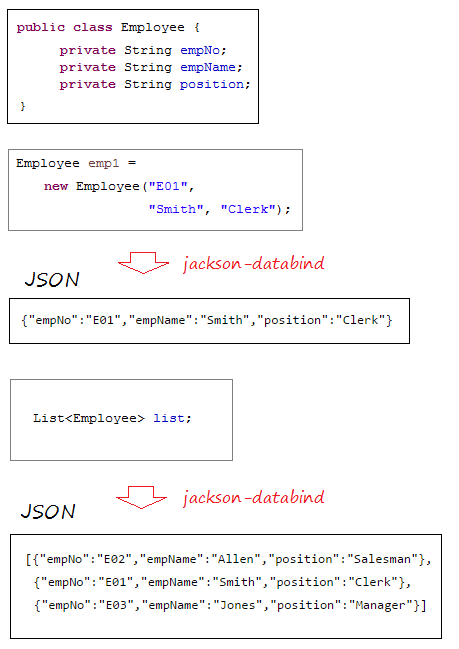
XML <==> Java
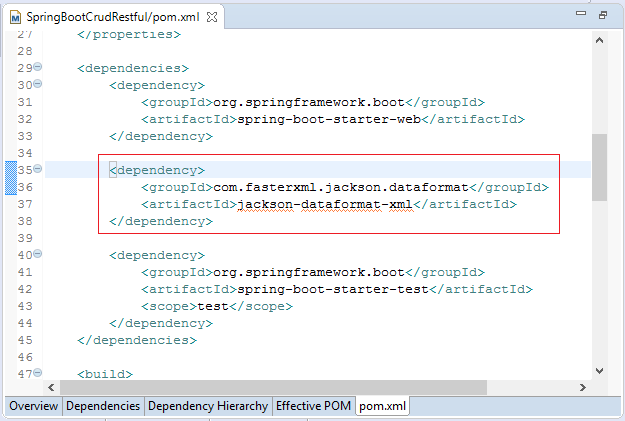
Spring Boot использует JAXB (Готовый в JDK) как библиотеку по умолчанию для конвертирования XML и Java. Но ваши классы Java должны быть аннотированы (annotated) с помощью @XmlRootElement,... Поэтому мой совет вам стоит использовать jackson-dataformat-xml как библиотеку для конвертирования XML и Java. Чтобы использовать jackson-dataformat-xml вам нужно объявить его в файле pom.xml:
** pom.xml **
...
<dependencies>
...
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformat</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-dataformat-xml</artifactId>
</dependency>
...
</dependencies>
...

pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0
http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>org.o7planning</groupId>
<artifactId>SbRestBasicAuthentication</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<name>SbRestBasicAuthentication</name>
<description>Spring Boot +Rest + Basic Authentication</description>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.0.0.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformat</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-dataformat-xml</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-security-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>4. Security & AuthenticationEntryPoint
Конфигурации безопасности будут написаны в классе WebSecurityConfig. В данной статье я не фокусируюсь на тему "Как получить username в базе данных", поэтому мы создаем 2 фиксированных UserName и сохраняем в памяти. Пользователь получает доступ в ресурс данных REST Service входит в систему с 1 из этих 2 username.
WebSecurityConfig.java
package org.o7planning.sbrestbasicauth.config;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.authentication.builders.AuthenticationManagerBuilder;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.authentication.configurers.provisioning.InMemoryUserDetailsManagerConfigurer;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.security.web.AuthenticationEntryPoint;
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class WebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
private AuthenticationEntryPoint authEntryPoint;
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.csrf().disable();
// All requests send to the Web Server request must be authenticated
http.authorizeRequests().anyRequest().authenticated();
// Use AuthenticationEntryPoint to authenticate user/password
http.httpBasic().authenticationEntryPoint(authEntryPoint);
}
@Bean
public BCryptPasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
BCryptPasswordEncoder bCryptPasswordEncoder = new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
return bCryptPasswordEncoder;
}
@Autowired
public void configureGlobal(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
String password = "123";
String encrytedPassword = this.passwordEncoder().encode(password);
System.out.println("Encoded password of 123=" + encrytedPassword);
InMemoryUserDetailsManagerConfigurer<AuthenticationManagerBuilder> //
mngConfig = auth.inMemoryAuthentication();
// Defines 2 users, stored in memory.
// ** Spring BOOT >= 2.x (Spring Security 5.x)
// Spring auto add ROLE_
UserDetails u1 = User.withUsername("tom").password(encrytedPassword).roles("USER").build();
UserDetails u2 = User.withUsername("jerry").password(encrytedPassword).roles("USER").build();
mngConfig.withUser(u1);
mngConfig.withUser(u2);
// If Spring BOOT < 2.x (Spring Security 4.x)):
// Spring auto add ROLE_
// mngConfig.withUser("tom").password("123").roles("USER");
// mngConfig.withUser("jerry").password("123").roles("USER");
}
}Класс AuthenticationEntryPointImpl расширен (extends) из класса BasicAuthenticationEntryPoint, он используется для проверки username/password прикрепленный к request действительный или нет.о
AuthenticationEntryPointImpl.java
package org.o7planning.sbrestbasicauth.auth;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.springframework.security.core.AuthenticationException;
import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.www.BasicAuthenticationEntryPoint;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class AuthenticationEntryPointImpl extends BasicAuthenticationEntryPoint {
@Override
public void commence(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, AuthenticationException authEx)
throws IOException, ServletException {
response.addHeader("WWW-Authenticate", "Basic realm=" + getRealmName());
response.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_UNAUTHORIZED);
PrintWriter writer = response.getWriter();
writer.println("HTTP Status 401 - " + authEx.getMessage());
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
// RealmName appears in the login window (Firefox).
setRealmName("o7planning");
super.afterPropertiesSet();
}
}5. Model, DAO, Controller
Класс Employee представляет сотрудника.
Employee.java
package org.o7planning.sbrestbasicauth.model;
public class Employee {
private String empNo;
private String empName;
private String position;
public Employee() {
}
public Employee(String empNo, String empName, String position) {
this.empNo = empNo;
this.empName = empName;
this.position = position;
}
public String getEmpNo() {
return empNo;
}
public void setEmpNo(String empNo) {
this.empNo = empNo;
}
public String getEmpName() {
return empName;
}
public void setEmpName(String empName) {
this.empName = empName;
}
public String getPosition() {
return position;
}
public void setPosition(String position) {
this.position = position;
}
}Класс EmployeeDAO аннотирован (annotate) с помощью @Repository, чтобы оповестить Spring, что он является Spring BEAN. Данный класс включает методы, помогающие дать запрос на список сотрудников (employee), создать сотрудника, изменить информацию сотрудника, и удалить сотрудника.
EmployeeDAO.java
package org.o7planning.sbrestbasicauth.dao;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import org.o7planning.sbrestbasicauth.model.Employee;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public class EmployeeDAO {
private static final Map<String, Employee> empMap = new HashMap<String, Employee>();
static {
initEmps();
}
private static void initEmps() {
Employee emp1 = new Employee("E01", "Smith", "Clerk");
Employee emp2 = new Employee("E02", "Allen", "Salesman");
Employee emp3 = new Employee("E03", "Jones", "Manager");
empMap.put(emp1.getEmpNo(), emp1);
empMap.put(emp2.getEmpNo(), emp2);
empMap.put(emp3.getEmpNo(), emp3);
}
public Employee getEmployee(String empNo) {
return empMap.get(empNo);
}
public Employee addEmployee(Employee emp) {
empMap.put(emp.getEmpNo(), emp);
return emp;
}
public Employee updateEmployee(Employee emp) {
empMap.put(emp.getEmpNo(), emp);
return emp;
}
public void deleteEmployee(String empNo) {
empMap.remove(empNo);
}
public List<Employee> getAllEmployees() {
Collection<Employee> c = empMap.values();
List<Employee> list = new ArrayList<Employee>();
list.addAll(c);
return list;
}
}Класс MainRESTController аннотирован (annotate) с помощью @RestController, чтобы оповестить Spring, что он является Spring Restful Controller,
MainRESTController.java
package org.o7planning.sbcrudrestful.controller;
import java.util.List;
import org.o7planning.sbcrudrestful.dao.EmployeeDAO;
import org.o7planning.sbcrudrestful.model.Employee;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class MainRESTController {
@Autowired
private EmployeeDAO employeeDAO;
@RequestMapping("/")
@ResponseBody
public String welcome() {
return "Welcome to RestTemplate Example.";
}
// URL:
// http://localhost:8080/SomeContextPath/employees
// http://localhost:8080/SomeContextPath/employees.xml
// http://localhost:8080/SomeContextPath/employees.json
@RequestMapping(value = "/employees", //
method = RequestMethod.GET, //
produces = { MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE, //
MediaType.APPLICATION_XML_VALUE })
@ResponseBody
public List<Employee> getEmployees() {
List<Employee> list = employeeDAO.getAllEmployees();
return list;
}
// URL:
// http://localhost:8080/SomeContextPath/employee/{empNo}
// http://localhost:8080/SomeContextPath/employee/{empNo}.xml
// http://localhost:8080/SomeContextPath/employee/{empNo}.json
@RequestMapping(value = "/employee/{empNo}", //
method = RequestMethod.GET, //
produces = { MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE, //
MediaType.APPLICATION_XML_VALUE })
@ResponseBody
public Employee getEmployee(@PathVariable("empNo") String empNo) {
return employeeDAO.getEmployee(empNo);
}
// URL:
// http://localhost:8080/SomeContextPath/employee
// http://localhost:8080/SomeContextPath/employee.xml
// http://localhost:8080/SomeContextPath/employee.json
@RequestMapping(value = "/employee", //
method = RequestMethod.POST, //
produces = { MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE, //
MediaType.APPLICATION_XML_VALUE })
@ResponseBody
public Employee addEmployee(@RequestBody Employee emp) {
System.out.println("(Service Side) Creating employee: " + emp.getEmpNo());
return employeeDAO.addEmployee(emp);
}
// URL:
// http://localhost:8080/SomeContextPath/employee
// http://localhost:8080/SomeContextPath/employee.xml
// http://localhost:8080/SomeContextPath/employee.json
@RequestMapping(value = "/employee", //
method = RequestMethod.PUT, //
produces = { MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE, //
MediaType.APPLICATION_XML_VALUE })
@ResponseBody
public Employee updateEmployee(@RequestBody Employee emp) {
System.out.println("(Service Side) Editing employee: " + emp.getEmpNo());
return employeeDAO.updateEmployee(emp);
}
// URL:
// http://localhost:8080/SomeContextPath/employee/{empNo}
@RequestMapping(value = "/employee/{empNo}", //
method = RequestMethod.DELETE, //
produces = { MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE, MediaType.APPLICATION_XML_VALUE })
@ResponseBody
public void deleteEmployee(@PathVariable("empNo") String empNo) {
System.out.println("(Service Side) Deleting employee: " + empNo);
employeeDAO.deleteEmployee(empNo);
}
}Объяснение:
- produces = { MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE, MediaType.APPLICATION_XML_VALUE }
- produces = { "application/json" , "application/xml" }
Атрибут produces используется, чтобы определить URL который будет создавать только (возвращать пользователю) данные с какими форматами. Например "application/json", "application/xml".
Руководства Java Web Services
- Что такое RESTful Web Service?
- Руководство Java RESTful Web Services для начинающих
- Простой пример CRUD с Java RESTful Web Service
- Создайте Java RESTful Client с помощью Jersey Client
- Отладчик RESTClient для RESTful WebServices
- Простой пример CRUD с Spring MVC RESTful Web Service
- Пример CRUD Restful Web Service c Spring Boot
- Пример Spring Boot Restful Client c RestTemplate
- Защита Spring Boot RESTful Service используя Basic Authentication
Show More
Руководства Spring Boot
- Установите Spring Tool Suite для Eclipse
- Руководство Spring для начинающих
- Руководство Spring Boot для начинающих
- Общие свойства Spring Boot
- Руководство Spring Boot и Thymeleaf
- Руководство Spring Boot и FreeMarker
- Руководство Spring Boot и Groovy
- Руководство Spring Boot и Mustache
- Руководство Spring Boot и JSP
- Руководство Spring Boot, Apache Tiles, JSP
- Используйте Logging в Spring Boot
- Мониторинг приложений с помощью Spring Boot Actuator
- Создание веб-приложения с несколькими языками с помощью Spring Boot
- Используйте несколько ViewResolver в Spring Boot
- Используйте Twitter Bootstrap в Spring Boot
- Руководство Spring Boot Interceptor
- Руководство Spring Boot, Spring JDBC и Spring Transaction
- Руководство Spring JDBC
- Руководство Spring Boot, JPA и Spring Transaction
- Руководство Spring Boot и Spring Data JPA
- Руководство Spring Boot, Hibernate и Spring Transaction
- Интеграция Spring Boot, JPA и H2 Database
- Руководство Spring Boot и MongoDB
- Используйте несколько DataSources с Spring Boot и JPA
- Используйте несколько DataSource с Spring Boot и RoutingDataSource
- Создайте приложение для входа с Spring Boot, Spring Security, Spring JDBC
- Создайте приложение для входа с Spring Boot, Spring Security, JPA
- Создайте приложение регистрации пользователей с помощью Spring Boot, Spring Form Validation
- Пример OAuth2 Social Login в Spring Boot.
- Запускать фоновые запланированные задачи в Spring
- Пример CRUD Restful Web Service c Spring Boot
- Пример Spring Boot Restful Client c RestTemplate
- Пример CRUD с Spring Boot, REST и AngularJS
- Защита Spring Boot RESTful Service используя Basic Authentication
- Защита Spring Boot RESTful Service используя Auth0 JWT
- Пример Upload file c Spring Boot
- Пример Download file c Spring Boot
- Пример Upload file c Spring Boot и jQuery Ajax
- Пример Upload file c Spring Boot и AngularJS
- Создание веб-приложения для корзины покупок с помощью Spring Boot, Hibernate
- Руководство Spring Email
- Создайте простое приложение Chat с Spring Boot и Websocket
- Разверните приложение Spring Boot на Tomcat Server
- Развертывание приложения Spring Boot на Oracle WebLogic Server
- Установите бесплатный сертификат Let's Encrypt SSL для Spring Boot
- Настройте Spring Boot для перенаправления HTTP на HTTPS
Show More