Руководство Java Reflection
1. Что такое Java Reflection?
Java использует слово "Java Reflection"чтобы наименовать важный API в стандартной библиотеке Java. Почему данный API был так назван? Давайте посмотрим объяснение данного значения.
Reflection является изображением отражения объекта. Например ваше отображение в зеркале, или отображение дерева на поверхности воды озера. Слово "Java Reflection" просто указывает другое изображение, другой подход у Java.

Java является объектно-ориентированным (Object-oriented) языком, обычно вам нужно создать объект и вы можете получить доступ в поля (field), или вызвать метод (method) данного объекта через точечный оператор ( . )
Java Reflection представляет другой подход, вы можете получить достуа в поле объекта, если вы знаете название того поля. Или вы можете вызвать метод объекта, если вы знаете название метода, виды параметров метода, и значения передаваемых параметров...
Java Reflecion позволяет вам оценивать, менять структуру и поведение объекта во время работы (runtime) программы. В то же время, он позволяет вам получить доступ к приватным членам (private member) везде в приложении, что не разрешается в традиционном подходе.
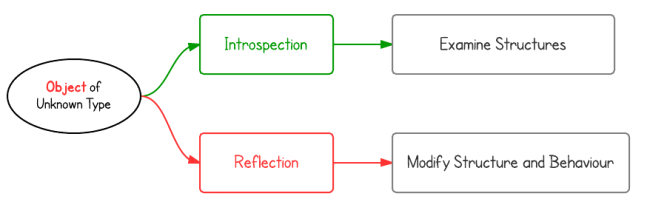
- Java обычно может называться Java Introspection (Интроспекция), программа имеет способность оценивать структуру объекта во время работы (Runtime).
- С Java Reflection, программа может оценивать структуру объекта во время работы, менять структуру и поведение объекта.
2. Неокоторые классы участвующие в примерах
Вот некоторые из классов, участвующих в примерах данной статьи.
Animal.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.beans;
public abstract class Animal {
public String getLocation() {
return "Earth";
}
public abstract int getNumberOfLegs() ;
}Say.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.beans;
public interface Say {
public String say();
}Cat.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.beans;
public class Cat extends Animal implements Say {
public static final String SAY = "Meo meo";
public static final int NUMBER_OF_LEGS = 4;
// Private field.
private String name;
// Private field
public int age;
public Cat() {
}
public Cat(String name) {
this.name = name;
this.age = 1;
}
public Cat(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
// Private Method.
private void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return this.age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
/**
* Implements from interface Say.
*/
@Override
public String say() {
return SAY;
}
/**
* Implements from Animal.
*/
@Override
public int getNumberOfLegs() {
return NUMBER_OF_LEGS;
}
}3. Начнем с простого примера
Вот простой пример извлечения списка публичных методов класса, включая методы, унаследованные от родительского класса, и интерфейсы.
ListMethod.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.reflect.helloreflect;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class ListMethod {
// Protected method
protected void info() {
}
public static void testMethod1() {
}
public void testMethod2() {
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Get a list of public methods of this class
// Include methods inherited from the parent class, or interface.
// Lấy ra danh sách các method public của class này
// Bao gồm các các method thừa kế từ class cha, hoặc các interface.
Method[] methods = ListMethod.class.getMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
System.out.println("Method " + method.getName());
}
}
}Запуск примера:
Method testMethod1
Method testMethod2
Method main
Method wait
Method wait
Method wait
Method equals
Method toString
Method hashCode
Method getClass
Method notify
Method notifyAll4. Class
Некоторые важные методы в Reflection, относящиеся к классу.
Пример выписывает основные сведения о классе, такие как имя класса, пакет (package), модификатор (modifier), ..
ShowClassInfo.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.reflect.clazz;
import java.lang.reflect.Modifier;
public final class ShowClassInfo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Get Class object represent ShowClassInfo class.
Class<ShowClassInfo> aClass = ShowClassInfo.class;
// Print out class name, including the package name.
System.out.println("Class Name= " + aClass.getName());
// Print out simple class name (without package name).
System.out.println("Simple Class Name= " + aClass.getSimpleName());
// Package info
Package pkg = aClass.getPackage();
System.out.println("Package Name = " + pkg.getName());
// Modifier
int modifiers = aClass.getModifiers();
boolean isPublic = Modifier.isPublic(modifiers);
boolean isInterface = Modifier.isInterface(modifiers);
boolean isAbstract = Modifier.isAbstract(modifiers);
boolean isFinal = Modifier.isFinal(modifiers);
// true
System.out.println("Is Public? " + isPublic);
// true
System.out.println("Is Final? " + isFinal);
// false
System.out.println("Is Interface? " + isInterface);
// false
System.out.println("Is Abstract? " + isAbstract);
}
}Запуск примера:
Class Name= org.o7planning.tutorial.reflect.clazz.ShowClassInfo
Simple Class Name= ShowClassInfo
Package Name = org.o7planning.tutorial.reflect.clazz
Is Public? true
Is Final? true
Is Interface? false
Is Abstract? falseПример для записи информации класса Cat, такого как имя класса, и интерфейсов, которые реализует этот класс.
ShowClassCatInfo.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.reflect.clazz;
import org.o7planning.tutorial.beans.Cat;
public class ShowClassCatInfo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// The Class object represent Cat class
Class<Cat> aClass = Cat.class;
// Class name
System.out.println("Simple Class Name = " + aClass.getSimpleName());
// Get the Class object represent parent of Cat class
Class<?> aSuperClass = aClass.getSuperclass();
System.out.println("Simple Class Name of Super class = "
+ aSuperClass.getSimpleName());
// Determines the interfaces implemented by the class
// or interface represented by this object.
Class<?>[] itfClasses = aClass.getInterfaces();
for (Class<?> itfClass : itfClasses) {
System.out.println("Interface: " + itfClass.getSimpleName());
}
}
}Запуск примера:
Simple Class Name = Cat
Simple Class Name of Super class = Animal
Interface: SayПример получения информации о конструкторе, методе, поле класса (только публичные), включая публичные методы, общедоступное поле, унаследованное от родительского класса, интерфейсы.
ShowMemberInfo.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.reflect.clazz;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import org.o7planning.tutorial.beans.Cat;
public class ShowMemberInfo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Get object represent Cat class.
Class<Cat> aClass = Cat.class;
// Get Constructor array of Cat.
Constructor<?>[] constructors = aClass.getConstructors();
System.out.println(" ==== CONSTRUCTORs: ===== ");
for (Constructor<?> constructor : constructors) {
System.out.println("Constructor: " + constructor.getName());
}
// Get a list of public method of Cat
// Include the methods inherited from the parent class and the interfaces
Method[] methods = aClass.getMethods();
System.out.println(" ==== METHODs: ====== ");
for (Method method : methods) {
System.out.println("Method: " + method.getName());
}
// Get the list of the public fields
// Include the fields inherited from the parent class, and the interfaces
Field[] fields = aClass.getFields();
System.out.println(" ==== FIELDs: ====== ");
for (Field field : fields) {
System.out.println("Field: " + field.getName());
}
}
}Результаты:
==== CONSTRUCTORs: =====
Constructor: org.o7planning.tutorial.beans.Cat
Constructor: org.o7planning.tutorial.beans.Cat
Constructor: org.o7planning.tutorial.beans.Cat
==== METHODs: ======
Method: getAge
Method: setAge
Method: say
Method: getNumberOfLegs
Method: getName
Method: getLocation
Method: wait
Method: wait
Method: wait
Method: equals
Method: toString
Method: hashCode
Method: getClass
Method: notify
Method: notifyAll
==== FIELDs: ======
Field: SAY
Field: NUMBER_OF_LEGS
Field: age5. Constructor
Пример получения конструктора (Constructor) с указанными параметрами. И записать информацию об этом конструкторе (constructor).
ConstructorExample.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.reflect.constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import org.o7planning.tutorial.beans.Cat;
public class ConstructorExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException,
SecurityException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException,
IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException {
// Get Class object represent Cat class.
Class<Cat> aClass = Cat.class;
// Get the Constructor object of the public constructor
// that matches the specified parameterTypes
Constructor<?> constructor = aClass.getConstructor(String.class,
int.class);
// Get parameter array of this constructor.
Class<?>[] paramClasses = constructor.getParameterTypes();
for (Class<?> paramClass : paramClasses) {
System.out.println("Param: " + paramClass.getSimpleName());
}
// Initialize the object in the usual way
Cat tom = new Cat("Tom", 3);
System.out
.println("Cat 1: " + tom.getName() + ", age =" + tom.getAge());
// Using Java reflection to create object
Cat tom2 = (Cat) constructor.newInstance("Tom", 2);
System.out.println("Cat 2: " + tom.getName() + ", age ="
+ tom2.getAge());
}
}Результаты запуска класса:
Param: String
Param: int
Cat 1: Tom, age =3
Cat 2: Tom, age =26. Field
В следующем примере извлекается поле (field) с указанным именем.
FieldExample.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.reflect.field;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import org.o7planning.tutorial.beans.Cat;
public class FieldExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchFieldException,
SecurityException, IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException {
// Get Class object represent Cat class
Class<Cat> aClass = Cat.class;
// Get Field object represent field 'NUMBER_OF_LEGS'.
Field field = aClass.getField("NUMBER_OF_LEGS");
Class<?> fieldType = field.getType();
System.out.println("Field type: " + fieldType.getSimpleName());
Field ageField = aClass.getField("age");
Cat tom = new Cat("Tom", 5);
// Returns the value of the field represented by this Field,
// on the specified object.
Integer age = (Integer) ageField.get(tom);
System.out.println("Age = " + age);
// Sets the field represented by this Field object on
// the specified object argument to the specified new value.
ageField.set(tom, 7);
System.out.println("New Age = "+ tom.getAge());
}
}Результаты запуска класса:
Field type: int
Age = 5
New Age = 77. Method
Пример получения метода с указанным именем и указанными параметрами. Запишите информацию об этом методе, такую как вид возвращаемого значения, список параметров, ...
MethodExample.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.reflect.method;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import org.o7planning.tutorial.beans.Cat;
public class MethodExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException,
SecurityException, IllegalAccessException,
IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException {
// Class object represent Cat class
Class<Cat> aClass = Cat.class;
// Method object represent getAge() method.
Method getAgeMethod = aClass.getMethod("getAge");
// return type of method.
Class<?> returnType= getAgeMethod.getReturnType();
System.out.println("Return type of getAge: "+ returnType.getSimpleName());
Cat tom = new Cat("Tom", 7);
// Call method 'getAge' way Reflect
// This is equivalent to calling: tom.getAge()
int age = (int) getAgeMethod.invoke(tom);
System.out.println("Age = " + age);
// Method object represent setAge(int) method of Cat class.
Method setAgeMethod = aClass.getMethod("setAge", int.class);
// Call method setAge(int) way Reflect
// This is equivalent to calling: tom.setAge(5)
setAgeMethod.invoke(tom, 5);
System.out.println("New Age = " + tom.getAge());
}
}Результаты запуска класса:
Return type of getAge: int
Age = 7
New Age = 58. Методы getter и setter
No ADS
В следующем примере перечислены методы public setter и public getter класса.
GetSetExample.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.reflect.getset;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import org.o7planning.tutorial.beans.Cat;
public class GetSetExample {
// Method is getter if names start with get, and no parameters.
public static boolean isGetter(Method method) {
if (!method.getName().startsWith("get")) {
return false;
}
if (method.getParameterTypes().length != 0) {
return false;
}
if (void.class.equals(method.getReturnType())) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
// Method is setter if names start with set, and only one parameter.
public static boolean isSetter(Method method) {
if (!method.getName().startsWith("set")) {
return false;
}
if (method.getParameterTypes().length != 1) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Class object represet Cat class
Class<Cat> aClass = Cat.class;
// public methods
Method[] methods = aClass.getMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
boolean isSetter = isSetter(method);
boolean isGetter = isGetter(method);
System.out.println("Method: " + method.getName());
System.out.println(" - Is Setter? " + isSetter);
System.out.println(" - Is Getter? " + isGetter);
}
}
}Результаты запуска программы:
Method: getName
- Is Setter? false
- Is Getter? true
Method: getNumberOfLegs
- Is Setter? false
- Is Getter? true
Method: getAge
- Is Setter? false
- Is Getter? true
Method: setAge
- Is Setter? true
- Is Getter? false
Method: say
- Is Setter? false
- Is Getter? false
Method: getLocation
- Is Setter? false
- Is Getter? true
Method: wait
- Is Setter? false
- Is Getter? false
Method: wait
- Is Setter? false
- Is Getter? false
Method: wait
- Is Setter? false
- Is Getter? false
Method: equals
- Is Setter? false
- Is Getter? false
Method: toString
- Is Setter? false
- Is Getter? false
Method: hashCode
- Is Setter? false
- Is Getter? false
Method: getClass
- Is Setter? false
- Is Getter? true
Method: notify
- Is Setter? false
- Is Getter? false
Method: notifyAll
- Is Setter? false
- Is Getter? false9. Доступ в приватный метод (private method), поле (field)
No ADS
Вы не можете получить доступ к методу или полю обычным способом, когда он приватный (private), компилятор java так же не разрешает это. Но с Java Reflection это абсолютно возможно.
AccessPrivateFieldExample.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.reflect.privateaccess;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import org.o7planning.tutorial.beans.Cat;
public class AccessPrivateFieldExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IllegalArgumentException,
IllegalAccessException, NoSuchFieldException, SecurityException {
// Class object represent Cat class
Class<Cat> aClass = Cat.class;
// Class.getField(String) get public field only.
// Use Class.getDeclaredField(String):
// Get the Field object of field declared in class.
Field private_nameField = aClass.getDeclaredField("name");
// Allows for access to private field.
// Avoid IllegalAccessException
private_nameField.setAccessible(true);
Cat tom = new Cat("Tom");
String fieldValue = (String) private_nameField.get(tom);
System.out.println("Value field name = " + fieldValue);
// Set new valud for 'name' field.
private_nameField.set(tom, "Tom Cat");
System.out.println("New name = " + tom.getName());
}
}Результаты запуска класса:
Value field name = Tom
New name = Tom CatСледующий пример - доступ к приватному (private) методу.
AccessPrivateMethodExample.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.reflect.privateaccess;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import org.o7planning.tutorial.beans.Cat;
public class AccessPrivateMethodExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException,
SecurityException, IllegalAccessException,
IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException {
// Class object represent Cat class.
Class<Cat> aClass = Cat.class;
// Class.getMethod(String) get public method only.
// Use Class.getDeclaredMethod(String):
// Get the Method object of method declared in class.
Method private_setNameMethod = aClass.getDeclaredMethod("setName",
String.class);
// Allows for access to private method.
// Avoid IllegalAccessException
private_setNameMethod.setAccessible(true);
Cat tom = new Cat("Tom");
// Call private method
private_setNameMethod.invoke(tom, "Tom Cat");
System.out.println("New name = " + tom.getName());
}
}Результаты:
New name = Tom Cat10. Annotation
No ADS
MyAnnotation.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.reflect.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
// Annotation can be used at runtime.
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
// Use for class, interface, method, field, parameter.
@Target({ ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.FIELD,
ElementType.PARAMETER })
public @interface MyAnnotation {
String name();
String value() default "";
}Пример Annotation (Аннотации) с классом:
ClassAnnotationExample.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.reflect.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
@MyAnnotation(name = "Table", value = "Employee")
public class ClassAnnotationExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Class<?> aClass = ClassAnnotationExample.class;
// Get array of the Annotation of class
Annotation[] annotations = aClass.getAnnotations();
for (Annotation ann : annotations) {
System.out.println("Annotation: " + ann.annotationType().getSimpleName());
}
// Or More specific
Annotation ann = aClass.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class);
MyAnnotation myAnn = (MyAnnotation) ann;
System.out.println("Name = " + myAnn.name());
System.out.println("Value = " + myAnn.value());
}
}Результаты:
Annotation: MyAnnotation
Name = Table
Value = EmployeeПример Annotation (Аннотация) с полем (field) и методом (Method):
FieldMethodAnnotationExample.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.reflect.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class FieldMethodAnnotationExample {
@MyAnnotation(name = "My Field")
private int myField;
@MyAnnotation(name = "My Method", value = "My Method Value")
protected void myMethod(String str) {
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchFieldException,
SecurityException, NoSuchMethodException {
Class<?> aClass = FieldMethodAnnotationExample.class;
//
System.out.println(" == FIELD == ");
Field field = aClass.getDeclaredField("myField");
// Get array of Annotation of field
Annotation[] fieldAnns = field.getAnnotations();
for (Annotation methodAnn : fieldAnns) {
System.out.println("Annotation: "
+ methodAnn.annotationType().getSimpleName());
}
// Or more specific
Annotation fieldAnn = field.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class);
MyAnnotation myAnn1 = (MyAnnotation) fieldAnn;
System.out.println("Name = " + myAnn1.name());
System.out.println("Value = " + myAnn1.value());
// Similar for method ...
System.out.println(" == METHOD == ");
Method method = aClass.getDeclaredMethod("myMethod", String.class);
// Get array of Annotation of method
Annotation[] methodAnns = method.getAnnotations();
for (Annotation methodAnn : methodAnns) {
System.out.println("Annotation: "
+ methodAnn.annotationType().getSimpleName());
}
// For more specific
Annotation methodAnn = method.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class);
MyAnnotation myAnn2 = (MyAnnotation) methodAnn;
System.out.println("Name = " + myAnn2.name());
System.out.println("Value = " + myAnn2.value());
}
}Результаты запуска:
== FIELD ==
Annotation: MyAnnotation
Name = My Field
Value =
== METHOD ==
Annotation: MyAnnotation
Name = My Method
Value = My Method ValueПример Annotation с параметром метода:
ParameterAnnotationExample.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.reflect.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class ParameterAnnotationExample {
// For example, a method with annotations in parameters.
protected void doSomething(int jobType,
@MyAnnotation(name = "Table", value = "Employee") String info) {
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException,
SecurityException {
Class<?> aClass = ParameterAnnotationExample.class;
// Get Method object of doSomething(int,String) method.
Method method = aClass.getDeclaredMethod("doSomething", int.class,
String.class);
// Get parameters list of method
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
for (Class<?> parameterType : parameterTypes) {
System.out.println("Parametete Type: "
+ parameterType.getSimpleName());
}
System.out.println(" ---- ");
// Returns an array of arrays of Annotations that
// represent the annotations on the formal parameters
Annotation[][] annotationss = method.getParameterAnnotations();
// Get Annotation list of parameter index 1.
Annotation[] annotations = annotationss[1];
for (Annotation ann : annotations) {
System.out.println("Annotation: "
+ ann.annotationType().getSimpleName());
}
}
}Parametete Type: int
Parametete Type: String
----
Annotation: MyAnnotationNo ADS
Java Basic
- Настройте java compiler для обработки вашего Annotation (Annotation Processing Tool)
- Программирование на Java для группы с помощью Eclipse и SVN
- Руководство Java WeakReference
- Руководство Java PhantomReference
- Сжатие и декомпрессия в Java
- Настройка Eclipse для использования JDK вместо JRE
- Методы String.format() и printf() в Java
- Синтаксис и новые функции в Java 8
- Регулярные выражения Java
- Руководство Java Multithreading Programming
- Библиотеки Java JDBC Driver для различных типов баз данных
- Руководство Java JDBC
- Получить значения столбцов, автоматически возрастающих при вставлении (Insert) записи, используя JDBC
- Руководство Java Stream
- Руководство Java Functional Interface
- Введение в Raspberry Pi
- Руководство Java Predicate
- Абстрактный класс и Interface в Java
- Модификатор доступа (Access modifiers) в Java
- Руководство Java Enum
- Руководство Java Annotation
- Сравнение и Сортировка в Java
- Руководство Java String, StringBuffer и StringBuilder
- Обработка исключений Java - Java Exception Handling
- Руководство Java Generics
- Манипулирование файлами и каталогами в Java
- Руководство Java BiPredicate
- Руководство Java Consumer
- Руководство Java BiConsumer
- Что мне нужно для начала работы с Java?
- История Java и разница между Oracle JDK и OpenJDK
- Установить Java в Windows
- Установите Java в Ubuntu
- Установите OpenJDK в Ubuntu
- Установить Eclipse
- Установите Eclipse в Ubuntu
- Быстрое изучение Java для начинающих
- История бит и байтов в информатике
- Типы данных в java
- Битовые операции
- Команда if else в Java
- команды switch в Java
- Циклы в Java
- Массивы (Array) в Java
- JDK Javadoc в формате CHM
- Наследование и полиморфизм в Java
- Руководство Java Function
- Руководство Java BiFunction
- Пример Java encoding и decoding с использованием Apache Base64
- Руководство Java Reflection
- Java Удаленный вызов методов - Java RMI
- Руководство Программирование Java Socket
- Какую платформу я должен выбрать для разработки приложений Java Desktop?
- Руководство Java Commons IO
- Руководство Java Commons Email
- Руководство Java Commons Logging
- Понимание Java System.identityHashCode, Object.hashCode и Object.equals
- Руководство Java SoftReference
- Руководство Java Supplier
- Аспектно-ориентированное программирование Java с помощью AspectJ (AOP)
Show More
- Руководства Java Servlet/JSP
- Руководства Java Collections Framework
- Java API для HTML, XML
- Руководства Java IO
- Руководства Java Date Time
- Руководства Spring Boot
- Руководства Maven
- Руководства Gradle
- Руководства Java Web Services
- Руководства Java SWT
- Руководства JavaFX
- Руководства Oracle Java ADF
- Руководства Struts2 Framework
- Руководства Spring Cloud